Nuclear medicine uses radioactive isotopes, also known as radioisotopes or radionuclides, to diagnose and treat disease. This specialized field of medicine is routinely employed at hospitals and health care facilities worldwide. It includes a wide range of medical procedures from positron emission tomography (PET) scans that diagnose Alzheimer’s disease to the administration of radiopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment.
Diagnostics: Imaging with Radioisotopes
Imaging with nuclear medicine is a powerful tool for diagnosing disease that uses radiotracers to visualize and assess bodily functions. To be safe and effective, the correct radioisotope must be pure and securely attached to the appropriate carrier molecule through a process called radiolabeling.
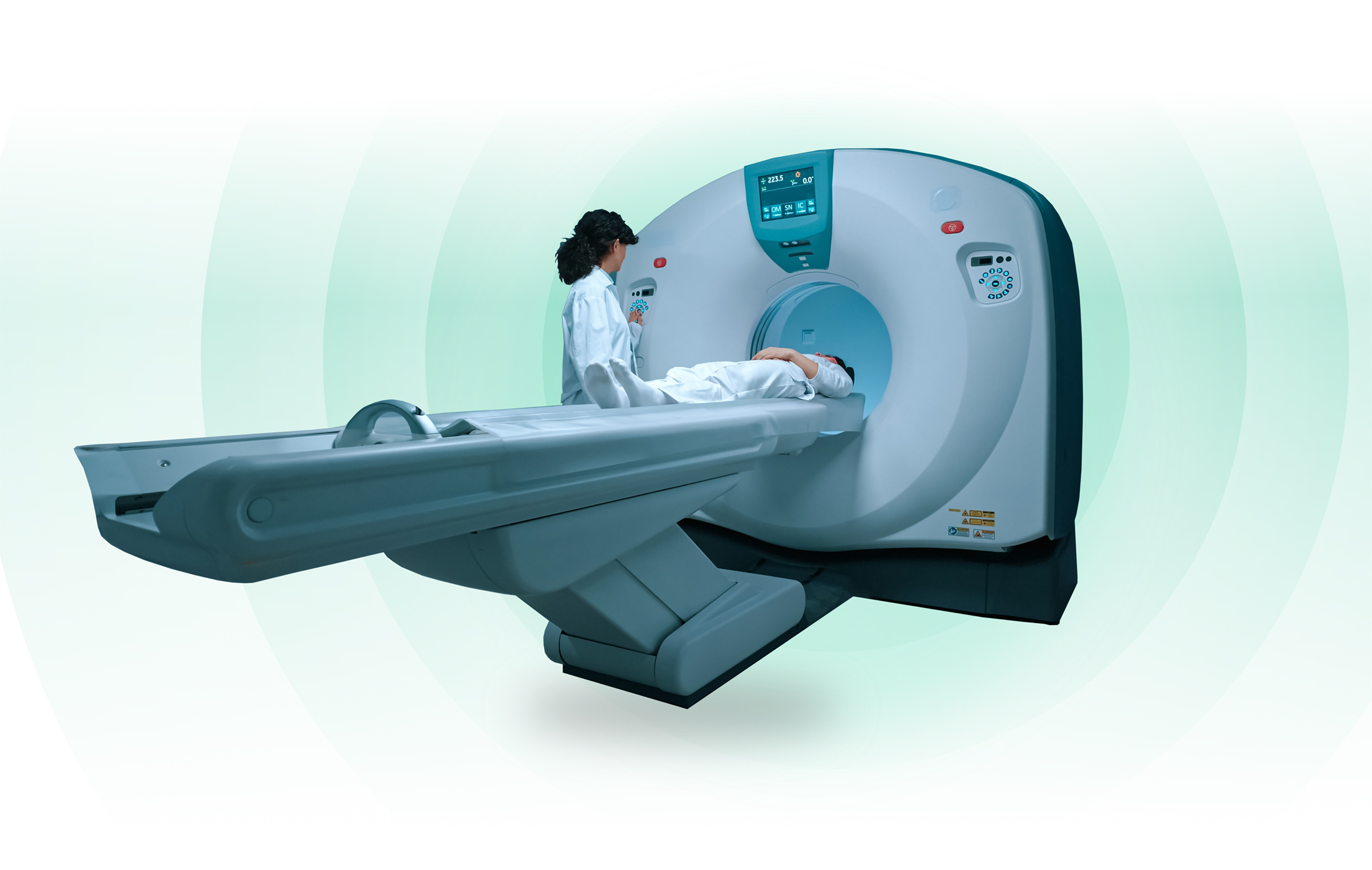
RadSep has technology to both purify radioisotopes and incorporate them into radiotracers. MRT™ resins to purify Cu-64, Pb-203 and other radioisotopes for imaging are readily available. RadSep also specializes in manufacturing high-quality macrocycles and chelating agents used in radiolabeling. For example, Cryptand 2.2.2 (MacroLig® 404) is a phase transfer reagent essential for the preparation of fluoro-deoxyglucose incorporating F-18, t½ = 1.8 h, as a tracer for PET imaging.
Therapeutics: Targeted Radionuclide Therapy (TRT) and Brachytherapy
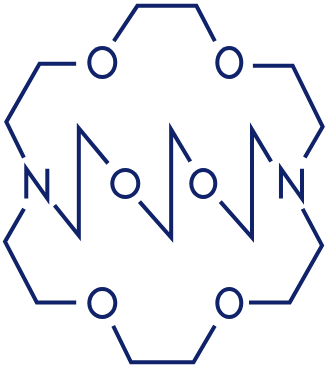
This image shows the scans of a patient with metastatic prostate cancer (A) before treatment (B) after 3 treatment cycles and (C) after a fourth treatment cycle with alpha-emitting 225Ac-PSMA-617. The dark spots in image A are cancerous growths. After 9 months of treatment, the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in the blood declined to non-detectable levels, indicative of complete remission.
Image Source: Kratochwil C, Bruchertseifer F, Giesel FL, et al. 225Ac-PSMA-617 for PSMA-targeted α-radiation therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2016; 57:1941–1944.
Targeted Radionuclide Therapy
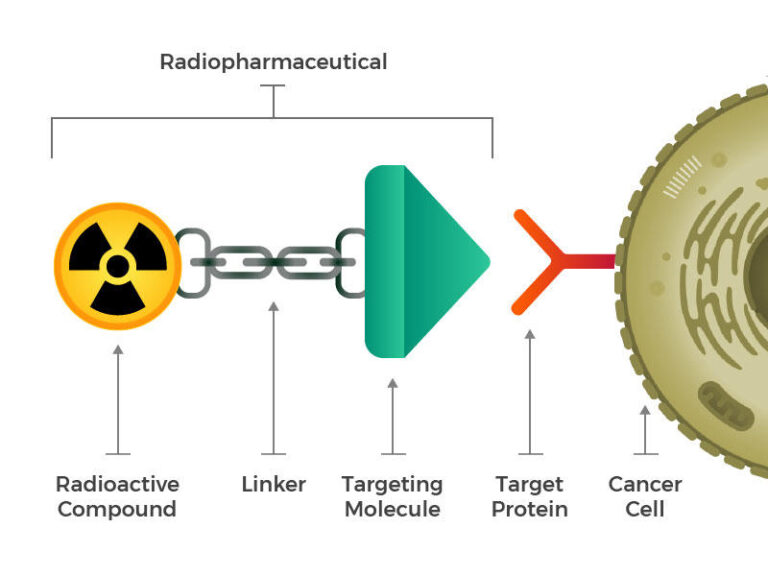
- A radioactive molecule made up of:
- A radionuclide that emits alpha or beta particles
- A chelating agent that strongly binds the radionuclide
- A targeting molecule that recognizes and binds to cancer cells
- A linker that connects the radioactive compound to the targeting molecule
Radiopharmaceuticals consist of a radioactive molecule, a targeting molecule, and a linker that joins the two.
Image Source: National Cancer Institute
Drugs for targeted radionuclide therapy are revolutionizing the treatment of cancer, especially radiopharmaceuticals for targeted alpha therapy (TAT). Alpha-emitting radionuclides (such as Ac-225 and the decay products of Pb-212) have two key advantages over beta-emitting radionuclides (such as Lu-177):
- More specific: alpha radiation has a shorter range than beta radiation in tissues, so it is less likely to damage healthy cells near the cancerous cells
- More powerful: alpha radiation has a higher linear energy transfer (LET) than beta radiation which can break both strands of DNA and result in cell death with very small doses of radiation
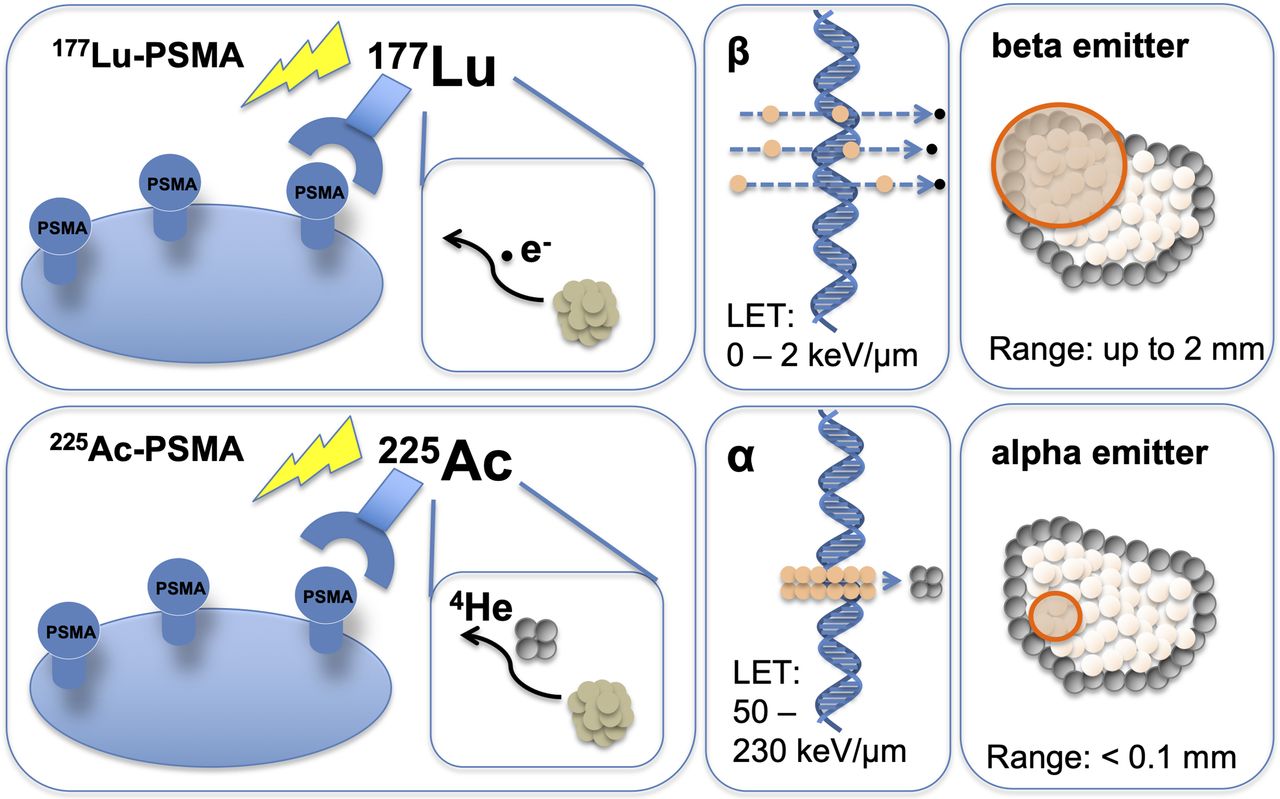
Image Source: Feuerecker B, Kratochwil C, Ahmadzadehfar H, et al.Clinical Translation of Targeted α-Therapy: An Evolution or a Revolution? J Nucl Med. 2023;64:685-692
By working at the cellular level to target specific cancer cells, targeted alpha therapy can administer massive radiation doses that have minimal effect on adjacent healthy cells. Of course, the safety of these radiopharmaceuticals depends on both the purity of the radioisotopes and the ability of the chelating agent to securely bind them so they are delivered directly to the cancer cells.
RadSep applies its expertise in highly selective radionuclide separations and finely tuned organic chemistry synthesis to supply both highly purified radionuclides and custom chelating agents for radionuclides. The high selectivity and high binding coefficients of RadSep’s separation and chelation products make them superior to traditional resins and chelators for radionuclides.
Brachytherapy
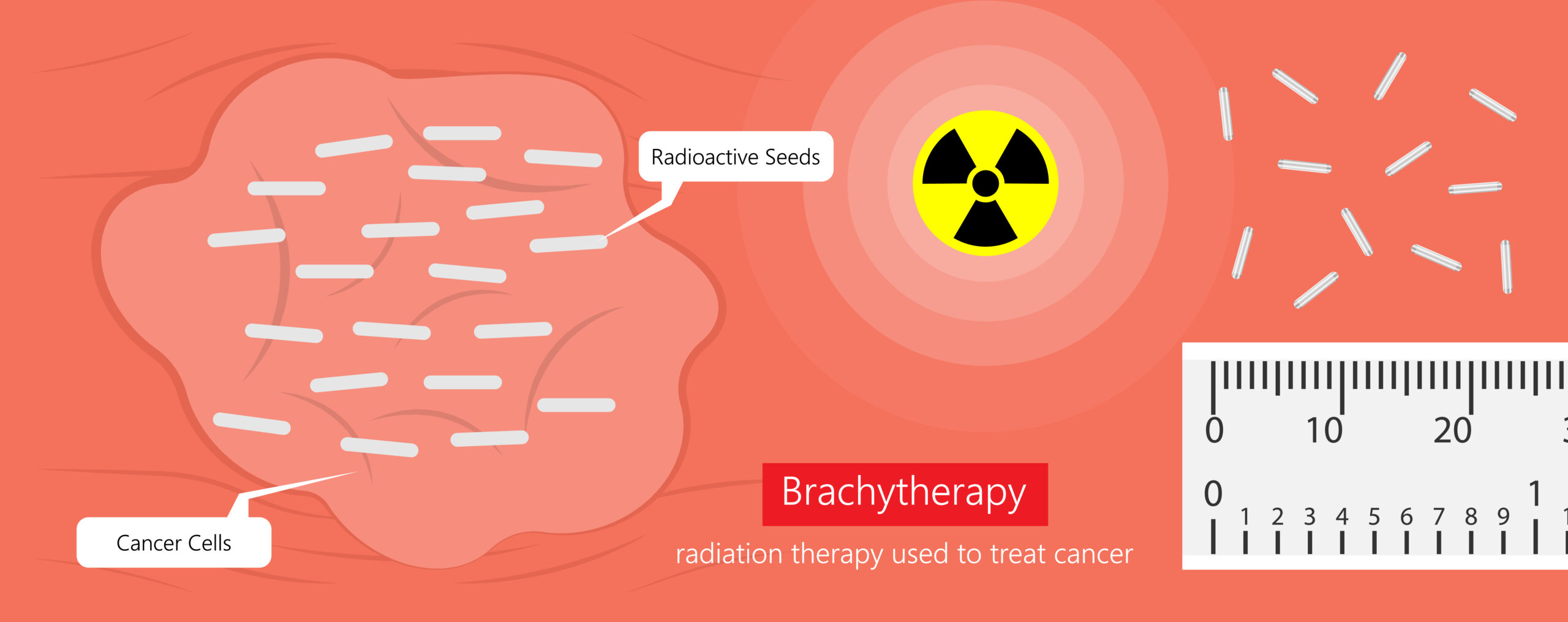
Brachytherapy, also known as internal radiation therapy, is a form of radiotherapy where a sealed radiation source is placed inside the patient, as close as possible to the area requiring treatment. It is commonly used to treat cancer, especially prostate cancer, by the insertion of radioactive palladium-103 (Pd-103) seeds directly into the tissue.
Molecular Recognition Technology™ (MRT™) is used to selectively separate and recover Pd-103 in the manufacture of brachytherapy seeds at Theragenics Corporation. High purity Pd-103, essential in this application, is easily obtained with a simplified flowsheet that eliminates steps, reagents, and waste production inherent in other separation processes.
MRT™ resins are also available for the highly selective separation of iridium-192 and cesium-131.